A survey paper published in IEEE Access
Paper Title
A Survey on Data Plane Flexibility and Programmability in Software-Defined Networking
Authors
- Enio Kaljic
- Department of Telecommunications, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, University of Sarajevo, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
-
- Department of Telecommunications, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, University of Sarajevo, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
-
- Department of Telecommunications, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, University of Sarajevo, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Mesud Hadzialic
- Department of Telecommunications, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, University of Sarajevo, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Abstract
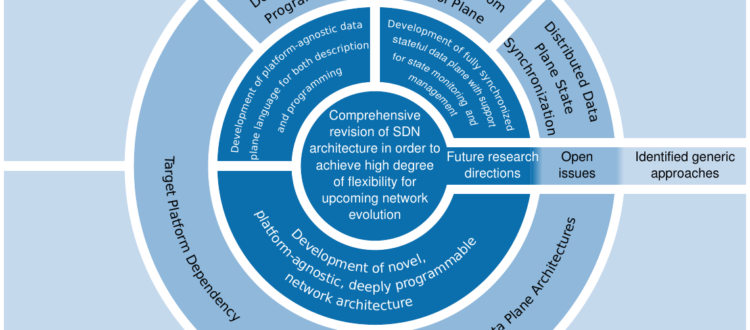
Software-defined networking (SDN) has attracted the attention of the research community in recent years, as evidenced by a large number of survey and review papers. The architecture of SDN clearly recognizes three planes: application, control, and data plane. The application plane executes network applications; control plane regulates the rules for the entire network based on the requests generated by network applications; and based on the set rules, the controller configures the switches in the data plane. The role of the switch in the data plane is to simply forward packets based on the instructions given by the controller. By analyzing SDN-related research papers, it is observed that research, from the very beginning, is insufficiently focused on the data plane. Therefore, this paper gives a comprehensive overview of the data plane survey with particular emphasis on the problem of programmability and flexibility. The first part of the survey is dedicated to the evaluation of actual data plane architectures through several definitions and aspects of data plane flexibility and programmability. Then, an overview of SDN-related research was presented with the aim of identifying key factors influencing the gradual deviation from the original data plane architectures given with ForCES and OpenFlow specifications. In this paper we used the term data plane evolution for this deviation. By establishing a correlation between the treated problem and the problem-solving approaches, the limitations of ForCES and OpenFlow data plane architectures were identified. Based on identified limitations, a generalization of approaches to addressing the problem of data plane flexibility and programmability has been made. By examining generalized approaches, open issues have been identified, establishing the grounds for future research directions proposal.
Keywords
Data plane;data plane abstractions;data plane architectures;data plane flexibility;data plane implementations;data plane languages;data plane programmability;deeply programmable networks;description languages;energy consumption;energy efficiency;hardware-based implementations;measurement;monitoring;network virtualization;network functions virtualization;networking technologies;performance;programming languages;quality of service;reliability;security;software-based implementations;software-defined networking;stateful data plane
Citation
E. Kaljic, A. Maric, P. Njemcevic and M. Hadzialic, “A Survey on Data Plane Flexibility and Programmability in Software-Defined Networking,” in IEEE Access. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2910140
Journal Title
IEEE Access
Electronic ISSN
2169-3536
Publisher
IEEE
Impact Factor
3.557 (2017)